1953 West German federal election
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 487 seats in the Bundestag[a] 244 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Registered | 33,120,940 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 28,479,550 (86.0%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
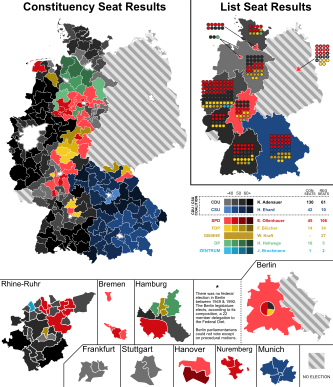 The left side shows the winning party vote in the constituencies, the right side shows the seats won by parties in each of the states. The pie chart over West Berlin shows the partisan composition of its legislature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Federal elections were held in West Germany on 6 September 1953 to elect the members of the second Bundestag. The Christian Democratic Union (CDU) emerged as the largest party.
This elections were the last before Saarland joined West Germany in 1957. It had been a separate entity, Saar protectorate, under French control since 1946.
The CDU/CSU formed a center-right coalition government with the FDP, DP and GB/BHE, leaving the SPD as the main opposition.[1] In comparison to the 1949 election where ten parties won seats, only six parties won seats in the 1953 election, thus entailing a consolidation of the party system.[1]
Campaign
[edit]Federal Chancellor Konrad Adenauer (who was also CDU leader) campaigned on his policies of economic reconstruction and growth, moderate conservatism or Christian democracy, and close relations with the United States. During the campaign he attacked the Social Democratic Party (SPD) ferociously. His staff had a comfortable coach on a train previously used only by Hermann Göring and behind that a dining car with sleeping berths for journalists.[2] The new SPD leader (Kurt Schumacher had died in 1952) was Erich Ollenhauer, who was more moderate in his policies than Schumacher had been. He did not oppose, in principle, the United States' military presence in Western Europe. He later – in 1957 – supported a military alliance of most European countries, including Germany.[3][4] On 3 September American Secretary of State John Foster Dulles said that "A defeat for Adenauer would have catastrophic consequences for the prospects for German reunification and the restoration of sovereignty" and that it would "trigger off such confusion in Germany that further delays in German efforts for reunification and freedom would be unavoidable."[2] Adenauer managed to convince clearly more West German voters of his leadership abilities and economic and political success to easily win a second term, although he had to form a coalition government with the Free Democratic Party and the conservative German Party to gain a majority in the Bundestag.
Results
[edit] | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Party-list | Constituency | Seats | |||||||||
| Votes | % | Seats | Votes | % | Seats | Elected | West Berlin | Total | +/– | |||
| Christian Democratic Union | 10,016,594 | 36.36 | 61 | 9,577,659 | 34.80 | 130 | 191 | 6 | 197 | +80 | ||
| Social Democratic Party | 7,944,943 | 28.84 | 106 | 8,131,257 | 29.55 | 45 | 151 | 11 | 162 | +26 | ||
| Free Democratic Party | 2,629,163 | 9.54 | 34 | 2,967,566 | 10.78 | 14 | 48 | 5 | 53 | 0 | ||
| Christian Social Union | 2,427,387 | 8.81 | 10 | 2,450,286 | 8.90 | 42 | 52 | 0 | 52 | +28 | ||
| All-German Bloc/League of Expellees and Deprived of Rights | 1,616,953 | 5.87 | 27 | 1,613,215 | 5.86 | 0 | 27 | 0 | 27 | New | ||
| German Party | 896,128 | 3.25 | 5 | 1,073,031 | 3.90 | 10 | 15 | 0 | 15 | −2 | ||
| Communist Party | 607,860 | 2.21 | 0 | 611,317 | 2.22 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −15 | ||
| Bavaria Party | 465,641 | 1.69 | 0 | 399,070 | 1.45 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −17 | ||
| All-German People's Party | 318,475 | 1.16 | 0 | 286,465 | 1.04 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | New | ||
| Deutsche Reichspartei | 295,739 | 1.07 | 0 | 204,725 | 0.74 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −5 | ||
| Centre Party | 217,078 | 0.79 | 2 | 55,835 | 0.20 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 3 | −7 | ||
| Dachverband der Nationalen Sammlung | 70,726 | 0.26 | 0 | 78,356 | 0.28 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | New | ||
| South Schleswig Voters' Association | 44,585 | 0.16 | 0 | 44,339 | 0.16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −1 | ||
| Schleswig-Holstein Farmers and Farmworkers Democracy | 6,269 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | New | |||||
| Patriotic Union | 2,531 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | New | |||||
| Party of the Good Germans | 654 | 0.00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | New | |||||
| Independents and voter groups | 17,185 | 0.06 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −3 | |||||
| Total | 27,551,272 | 100.00 | 245 | 27,519,760 | 100.00 | 242 | 487 | 22 | 509 | +99 | ||
| Valid votes | 27,551,272 | 96.74 | 27,519,760 | 96.63 | ||||||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 928,278 | 3.26 | 959,790 | 3.37 | ||||||||
| Total votes | 28,479,550 | 100.00 | 28,479,550 | 100.00 | ||||||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 33,120,940 | 85.99 | 33,120,940 | 85.99 | ||||||||
| Source: Bundeswahlleiter | ||||||||||||
Results by state
[edit]Constituency seats
[edit]| State | Total seats |
Seats won | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDU | SPD | CSU | FDP | DP | DZP | ||
| Baden-Württemberg | 33 | 29 | 2 | 2 | |||
| Bavaria | 47 | 3 | 42 | 2 | |||
| Bremen | 3 | 3 | |||||
| Hamburg | 8 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | ||
| Hesse | 22 | 7 | 10 | 5 | |||
| Lower Saxony | 34 | 13 | 11 | 2 | 8 | ||
| North Rhine-Westphalia | 66 | 51 | 13 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Rhineland-Palatinate | 15 | 13 | 2 | ||||
| Schleswig-Holstein | 14 | 14 | |||||
| Total | 242 | 130 | 59 | 42 | 14 | 10 | 1 |
| This article is part of a series on the |
| Politics of Germany |
|---|
 |
List seats
[edit]| State | Total seats |
Seats won | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPD | CDU | FDP | GB/ BHE |
CSU | DP | DZP | ||
| Baden-Württemberg | 34 | 14 | 9 | 7 | 3 | 1 | ||
| Bavaria | 44 | 22 | 4 | 8 | 10 | |||
| Bremen | 3 | 2 | 1 | |||||
| Hamburg | 10 | 6 | 4 | |||||
| Hesse | 22 | 6 | 8 | 4 | 3 | 1 | ||
| Lower Saxony | 32 | 10 | 12 | 3 | 7 | |||
| North Rhine-Westphalia | 72 | 34 | 21 | 11 | 3 | 1 | 2 | |
| Rhineland-Palatinate | 16 | 7 | 5 | 4 | ||||
| Schleswig-Holstein | 12 | 7 | 1 | 3 | 1 | |||
| Total | 245 | 106 | 61 | 34 | 27 | 10 | 5 | 2 |
Aftermath
[edit]Konrad Adenauer remained Chancellor, governing in a broad coalition (two-thirds majority) with most of the minor parties except for the SPD and Centre Party.
Notes
[edit]- ^ As well as the 22 non-voting delegates for West Berlin, elected by the West Berlin Legislature.
- ^ As well as 6 non-voting delegates for West Berlin.
- ^ As well as 11 non-voting delegates for West Berlin.
- ^ As well as 5 non-voting delegates for West Berlin.
References
[edit]- ^ a b Barnes, Samuel H.; Grace, Frank; Pollock, James K.; Sperlich, Peter W. (1962). "The German Party System and the 1961 Federal Election". American Political Science Review. 56 (4): 899–914. doi:10.2307/1952792. ISSN 1537-5943.
- ^ a b Charles Williams (2000) Adenauer: The Father of the New Germany, p407
- ^ Erling Bjöl, Grimberg's History of the Nations, volume 23: The Rich West, "A Giant Dwarf: West Germany," Helsinki: WSOY, 1985
- ^ Dennis L. Bark and David R. Gress, A History of West Germany: Volume 1: 1945–1963: From Shadow to Substance, London, UK: Basil Blackwell, 1989




